Map of Yemen, Arabian Peninsula
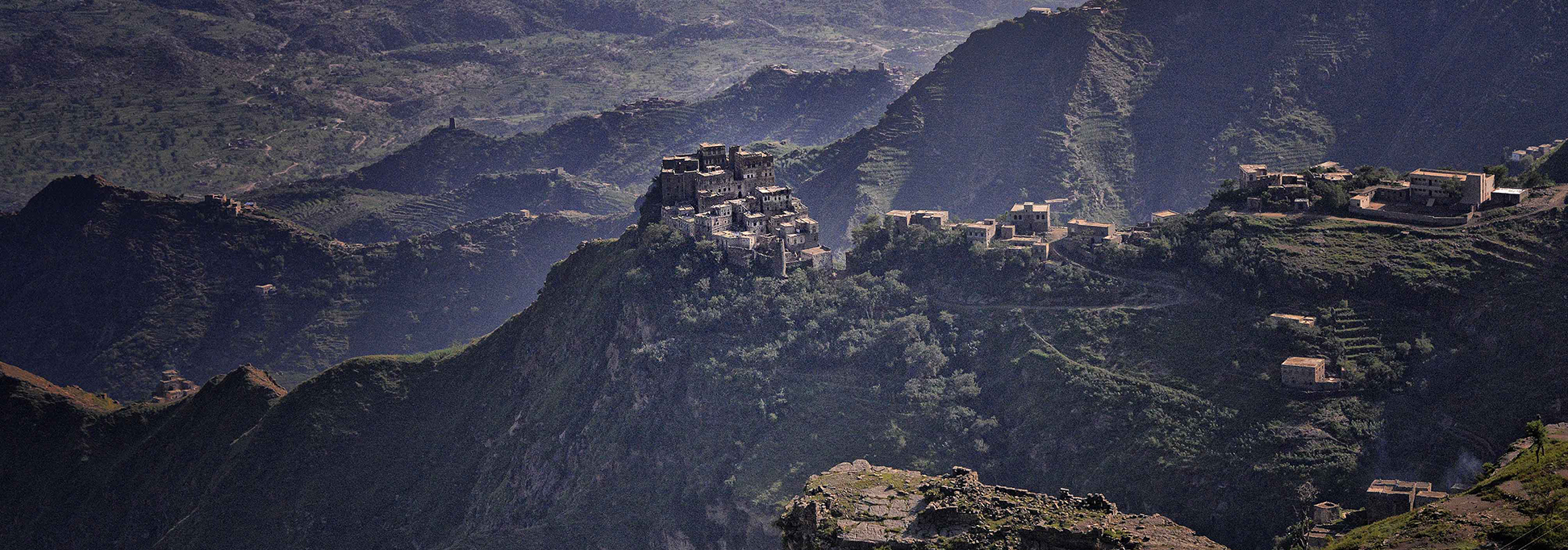

Jabal Haraz - the mountainous region between Sana'a and the port city of Al-Hudaydah. In the 11th century, it was the stronghold of the Sulaihid dynasty, in present-day it is Houthi occupied territory.
Image: Rod Waddington
About Yemen

Area
Yemen occupies an area of 527,970 km² (including the islands of Perim and Socotra), compared it is slightly smaller than Metropolitan France or about twice the size of the US state of Wyoming.
Yemen has a population of estimated 27.5 million people. The capital and largest city is Sana'a. Due to the control of Sana'a by Houthi rebels, the Yemeni seat of government moved first to Aden and in 2019 to Seiyun (Saywun) in the Hadhramaut region in the center of the country.
Spoken language is Yemeni Arabic. The main religion is Islam; two principal Islamic religious groups are present in the country, followers of Shia Islam predominantly inhabit the region between Sa'dah, the former capital Sana'a and Dhamar, the population in the coastal areas are mainly adherents of Sunni Islam.
Map of Yemen
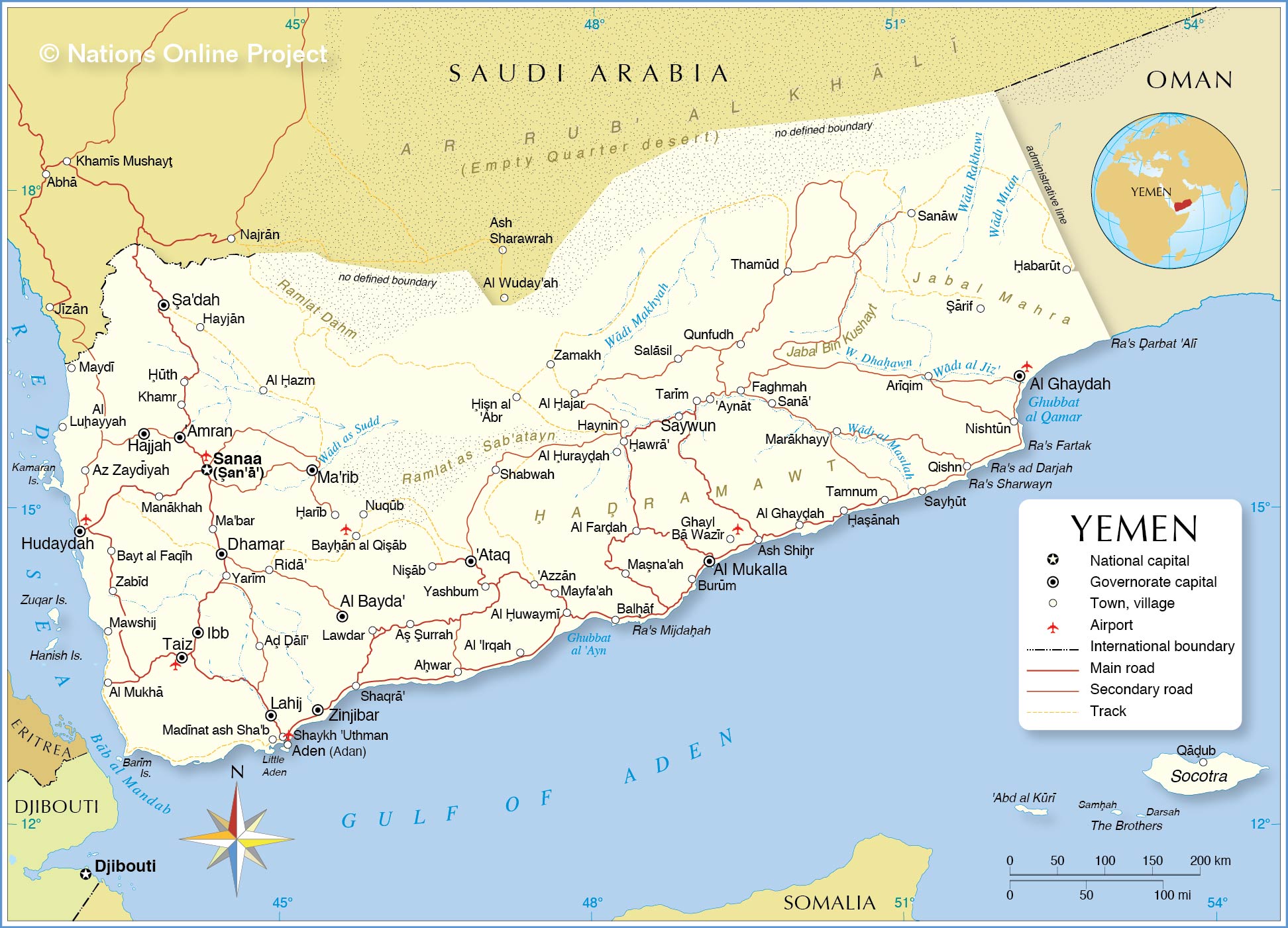
Political Map of Yemen
The map shows Yemen and surrounding countries with international borders, the national capital Sana'a, governorate capitals, major cities, main roads, railroads, and major airports.
 You are free to use above map for educational purposes (fair use), please refer to the Nations Online Project.
You are free to use above map for educational purposes (fair use), please refer to the Nations Online Project.

Political Map of Yemen
The map shows Yemen and surrounding countries with international borders, the national capital Sana'a, governorate capitals, major cities, main roads, railroads, and major airports.
More about Yemen
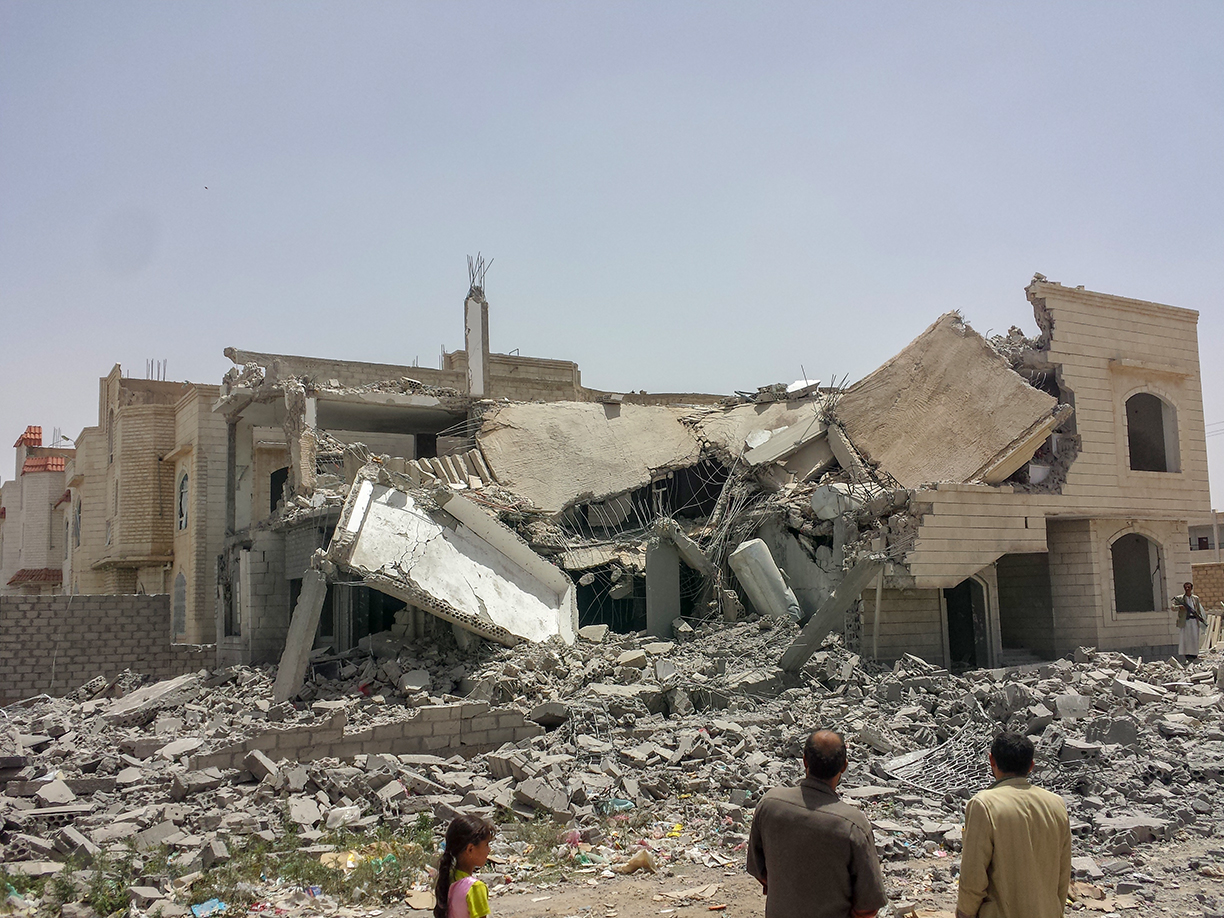

Destroyed house in Sanaa hit by a Saudi-led air strike on Sana'a, 12 June 2015. Saudi Arabia is operating without a UN mandate.
Photo: Ibrahem Qasim
Yemen covers the most mountainous portion of the Arabian Peninsula. The Asir mountains and their foothills dominate the western part of the country. Between the Red Sea and the mountains is the Tihamah, a narrow semidesert coastal plain, part of the Arabian Peninsula's coastal fog desert ecoregion which stretches further along the southern coast of the country.
The Rub' al-Khali, the largest contiguous sand desert, also known as the Empty Quarter, reaches into the northeastern part of the country. In the southeast of Yemen, there are the Mahra mountains (Jabal Mahra) with elevations up to 1300 m.
The country's interior is dominated by mountains ranging from a few hundred meters up to the country’s highest point, Jabal An-Nabi Shu'ayb at 3,666 m (12,028 ft).
The hills can be distinguished into the western highlands with relatively fertile soil and sufficient rainfall, and the central highland, more like a plateau of about 2,000-3,200 meters, with rolling hills, small mountains, and some very prominent peaks. The central highlands are drier than the western highlands because of rain-shadow influences but still receives sufficient rain in wet years for extensive cropping.
Yemen has no permanent rivers. The highland regions are interspersed with wadis, valleys with seasonal formed rivers; those rivers run almost completely dry in the summer months. Notable is the Wadi Hadhramaut (Hadramawt) in southern central Yemen, the upper parts of the wadi contain alluvial soil and floodwaters, and the lower part is barren and mostly uninhabited.
Most of the northern part of the country is covered by the "Empty Quarter" (Ar Rub' al Khali), one of the largest sand deserts in the world, encompassing most of the southern third of the Arabian Peninsula. Ramlat al-Sab`atayn is another desert region in central Yemen and a sparsely populated area. Further northeast is the vast Ramlat Dahm, a desert region and part of the "Empty Quarter."
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Comments
Post a Comment